Making diagnoses according to the latest scientific findings
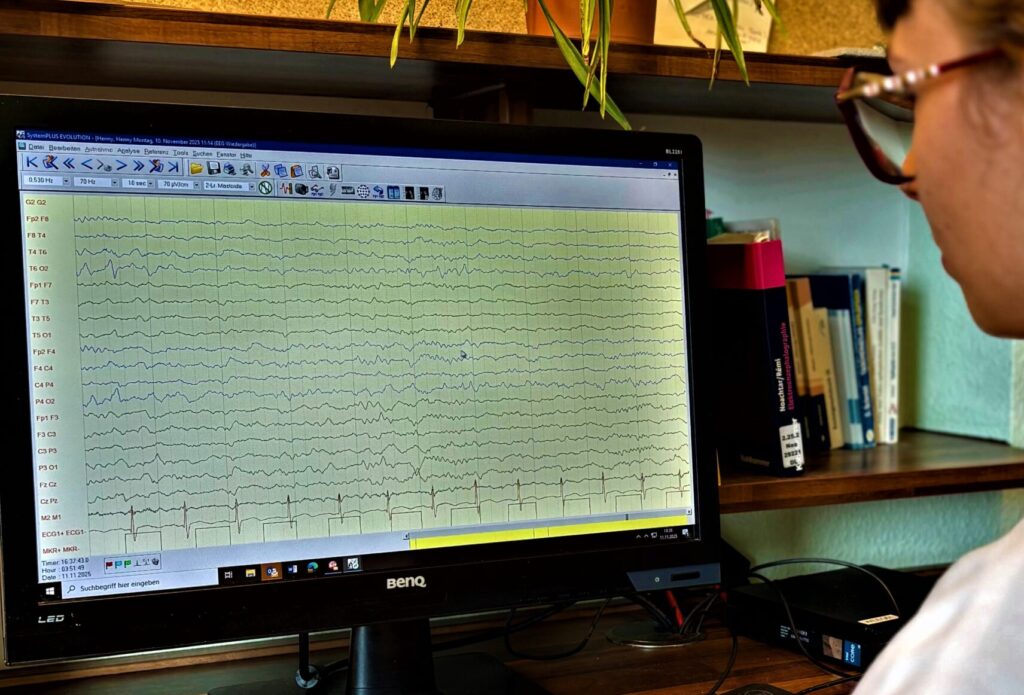
The Electroencephalogram, short EEG is a non-invasive method for measuring the electrical activity of the brain. Although it has been in use for over 100 years, it is the only method that can detect the hyperexcitability of the brain in patients with epilepsy and is constantly being further developed. It is therefore particularly suitable for Clarification of epilepsies, Impairment of consciousness or sleep disorders. The brain waves are first recorded for 20 minutes using electrodes attached to the scalp and then analysed. The EEG can provide valuable information about possible Malfunctions in the central nervous system.
A precise diagnosis is the first step towards treatment in neurology and epileptology in order to be able to act precisely on symptoms and causes.
Our EEG system will be completely modernised and brought up to date in 2026.
EEG - Regular routine EEG - Insight into brain activity
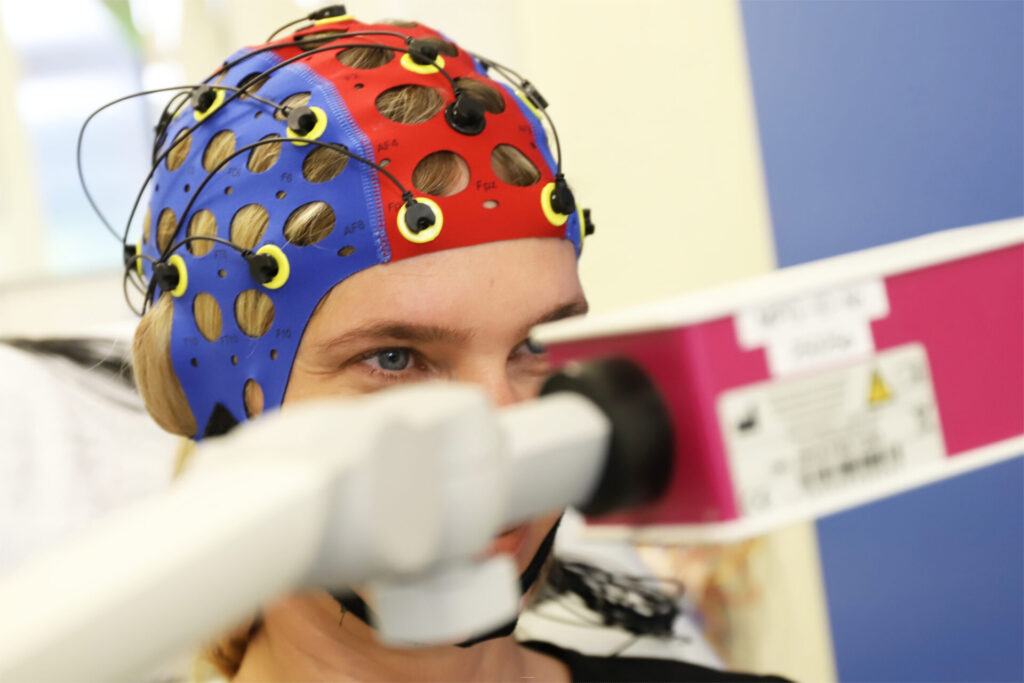
In the outpatient department and also in the inpatient area, a routine EEG is initially recorded while the patient is awake and ideally dozes off or even falls asleep during the recording. Electrodes are attached to certain measured points on the head with the aid of a cap.
Once all electrodes are in place and the recording conditions are correct, the actual recording can begin, which is normally 20 minutes lasts.
It is not uncommon for the EEG to be normal even in people with frequent seizures. This is due to the fact that, on the one hand, the EEG is only a Snapshot and can look completely different immediately after the derivation. Another reason for this is that only Changes in the EEG which generate an electrical field over the outer surface of the brain. It can therefore be useful to carry out repeated recordings. During these recordings, provocation methods (flickering light stimulation, hyperventilation) are also carried out in order to recognise typical EEG changes more likely in epilepsy patients.
Mobile long-term EEG: portable during hospitalisation
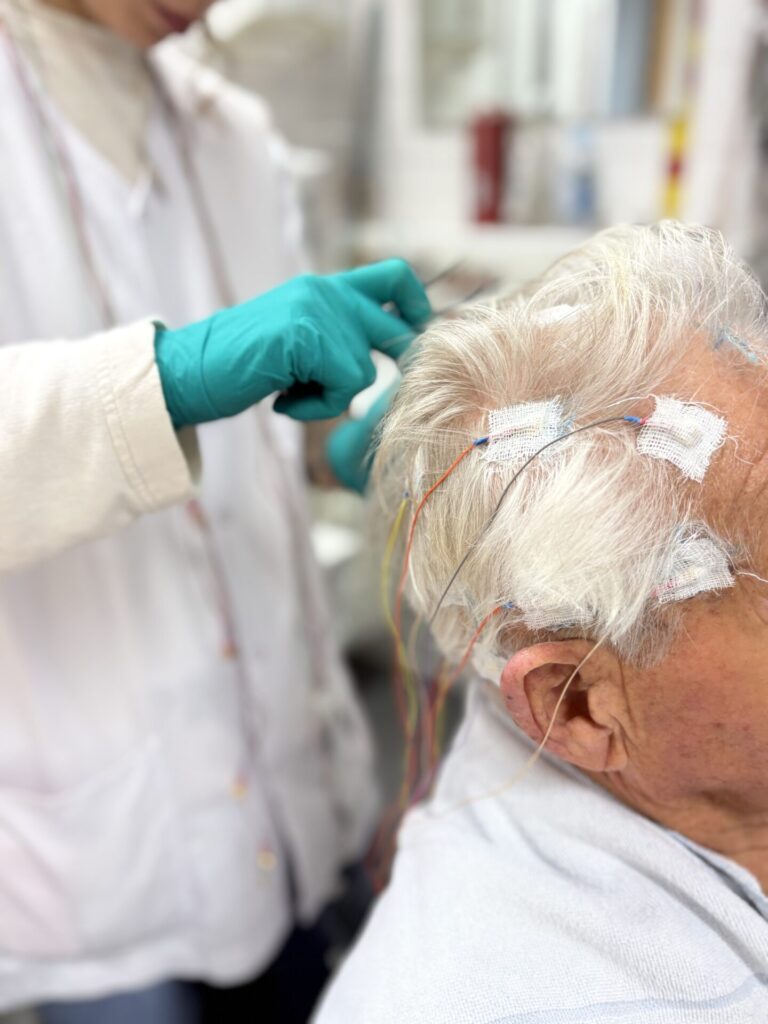
EEG technology has now been developed to such an extent that a small portable device can be used to obtain a Fully-fledged EEG can be recorded over a period of 24 hours. Different electrodes are used for this than in routine EEG. These are attached to the scalp with a collodion adhesive and removed again with acetone after the recording.
These Examination method is particularly suitable for recording the EEG during sleep. As with many Epilepsies Since the epilepsy-typical potentials are predominantly visible during sleep, this method is particularly suitable when it comes to the question of whether it can be assumed that epilepsy has started after a first seizure. It may also be possible to register seizures on the EEG.
Continuous video EEG diagnostics
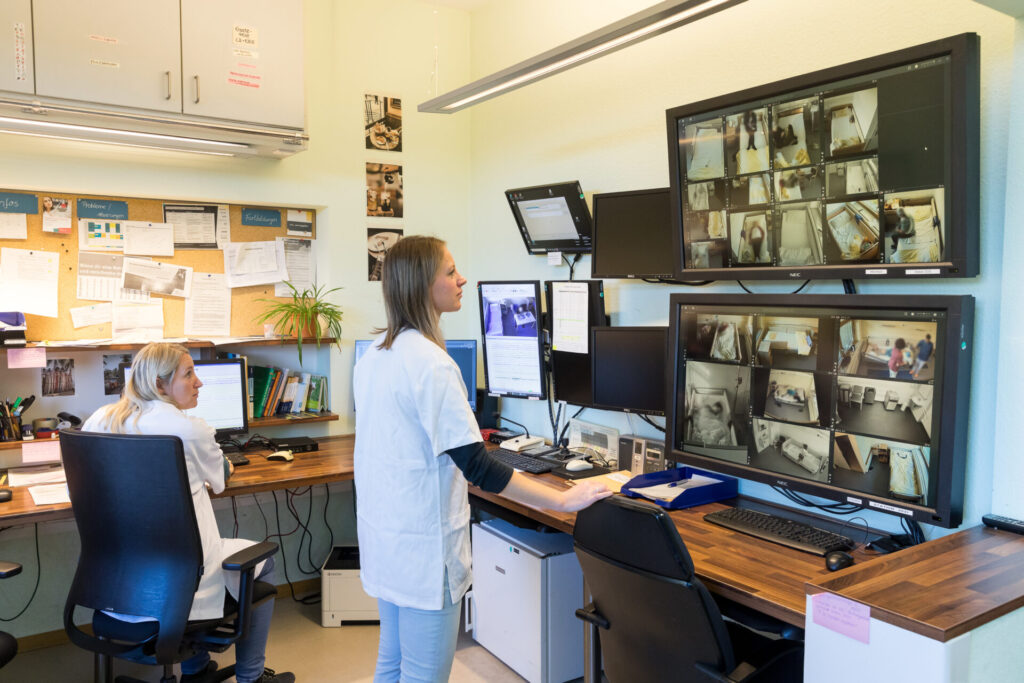
If seizures occur frequently and there is uncertainty as to whether these seizures are really epileptic, it can be helpful to Seizures simultaneously in video and EEG monitoring to record.
Thanks to the continuous Video EEG-Monitoring it is possible to carefully analyse the seizure sequence in the video together with the EEG to ensure the diagnosis.
This type of diagnosis is of particular importance when it comes to the question of whether there is an alternative for patients with epilepsy that cannot be adequately treated with medication (pharmacoresistant). Surgical treatment option or a possibility for a Neurostimulation procedure are present. Further special examinations are required here, whereby the basis of the diagnosis is initially the recording of seizures in the video EEG.

EEG in our clinic

contact
13:00 - 16:00